Author's posts
Mar 08 2013
Changing The Name But Not The Game: Up Dated x 2
Cross posted from The Stars Hollow Gazette
Or as Shakespeare’s Juliet said, “what’s in a name? that which we call a rose; By any other name would smell as sweet.” Not quite.
In this case calling chained CPI, “superlative CPI to make it more palatable to the voters and politicians who oppose it as a cut to future Social Security benefit, does not make it any less noxious or toxic:
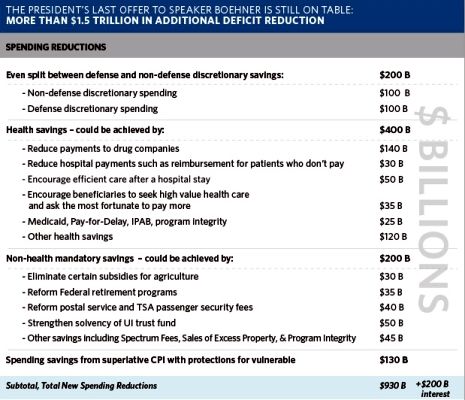
Click image to view it in full size
Spending savings from superlative CPI with protections for vulnerable $130 B
As Pres. Obama’s idol, Pres. Lincoln said, “You can fool some of the people all of the time, and all of the people some of the time, but you can not fool all of the people all of the time.”
No, Barack, we will not be fooled by you.
Up Date: 3/3/13 23:18 AM EST: Post and learn. It seems that there is a “superlative CPI”, from letgetitdone in a comment at Corrente:
Hi TMC, There is a “superlativeCPI ,” but it’s not “the chained CPI” which is really “the Catfood CPI.” An actual superlative CPI, would cost adjust for the higher proportion of seniors’ household budget they must spend on rapidly increasing health care costs. It would also adjust for living area. so that seniors who live in high cost areas, can remain there if they choose, rather than moving to lower cost areas where their meagre SS pensions don’t go very far. In the real world, living costs in New York City are 2 1/2 times more than living costs in say, rural Kansas or the UP of Michigan. SS payments should be adjusted for these important regional differences.
Up Date: 3/6/13 12:39 AM EST A cut is a cut. I want to thank Hugh at Corrente for this explanation.
Then there is the Chained CPI which is a modification of the CPI-U. It is being pushed by the anti-old, austerity-minded as a replacement for the particular version of the CPI-W I just described above which already tends to understate inflationary effects on Social Security recipients. And there is the annoying Administration reference to it as the superlative CPI. Again context is important. The CPI survey collects information on prices. These are first averaged individually by geographic area. This is called “lower-level aggregation”. The example which they use is the price of one item (apples) in one locality (Chicago). The BLS then does what it calls “higher-level aggregation” (note the use of the comparative): the price of apples regionally and nationally, the price of food nationally, the price of all items nationally, etc. The Chained CPI involves another level of analysis and what must follow the comparative but the superlative? (..)
http://www.bls.gov/cpi/cpisupq…
The example used is that the CPI-U and the CPI-W have prices for pork and beef. What the Chained CPI seeks to measure is, in the event of a price increase in pork, the effect of consumers switching to beef. The BLS example is, of course, innocuous. The one some of us are more concerned about is seniors being forced to choose between beef and cat food. Substitution basically reduces the effects of inflation. Calculating a CPI based on it will inherently be lower then others (CPI-U and CPI-W) which do not. What it ignores, some would say deliberately, is quality of life. (..)
http://www.bls.gov/cpi/cpieart…
What is important to understand is that the various schemes to cut the size of the Social Security COLA, including the one currently in place are cumulative. You have no doubt heard of the miracle of compound interest. Well, what these schemes amount to is negative compound interest being charged against our seniors. What is always left off the table is the question of what constitutes a living retirement, perhaps because it would lead to the related discussion of what constitutes a living wage. Instead we get a numbers game, divorced from the very social issue the number is supposed to address.
Mar 08 2013
Today on The Stars Hollow Gazette

Our regular featured content-
- On This Day In History March 7 by TheMomCat
- Punting the Pundit by TheMomCat
These featured articles-
- Changing The Name But Not The Game: Up Dated x 2 by TheMomCat
- Answer the question, Mr. President by joanneleon
- Well, this is not at all encouraging. by ek hornbeck
Follow us on Twitter @StarsHollowGzt
Write more and often. This is an Open Thread.
Mar 07 2013
On This Day In History March 7
Cross posted from The Stars Hollow Gazette
This is your morning Open Thread. Pour your favorite beverage and review the past and comment on the future.
Find the past “On This Day in History” here.
March 7 is the 66th day of the year (67th in leap years) in the Gregorian calendar. There are 299 days remaining until the end of the year.
On this day in 1965, a group of 600 civil rights marchers are forcefully broken up in Selma, Alabama. This day would be remembered in the Civil Rights Movement as “Bloody Sunday”
The Selma to Montgomery marches were three marches in 1965 that marked the political and emotional peak of the American civil rights movement. They grew out of the voting rights movement in Selma, Alabama, launched by local African-Americans who formed the Dallas County Voters League (DCVL). In 1963, the DCVL and organizers from the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC) began voter-registration work. When white resistance to Black voter registration proved intractable, the DCVL requested the assistance of Martin Luther King, Jr. and the Southern Christian Leadership Conference, who brought many prominent civil rights and civic leaders to support voting rights.
The first march took place on March 7, 1965 – “Bloody Sunday” – when 600 civil rights marchers were attacked by state and local police with billy clubs and tear gas. The second march took place on March 9. Only the third march, which began on March 21 and lasted five days, made it to Montgomery, 51 miles away.
The marchers averaged 10 miles a day along U.S. Route 80, known in Alabama as the “Jefferson Davis Highway”. Protected by 2,000 soldiers of the U.S. Army, 1,900 members of the Alabama National Guard under Federal command, and many FBI agents and Federal Marshals, they arrived in Montgomery on March 24, and at the Alabama Capitol building on March 25.
The route is memorialized as the Selma To Montgomery Voting Rights Trail, a U.S. National Historic Trail.
Selma essentially became the focus the right to vote marches because it was the seat of Dallas County, AL that although it has a black population of 57% with 15,000 blacks elegible to vote, there were only 130 registered. Efforts to register voters were blocked by state and local officials, the White Citizens’ Council, and the Ku Klux Klan, using a literacy test, economic pressure, and violence.
On July 2, 1964, President Lyndon B. Johnson signed the Civil Rights Act of 1964 into law, which declared segregation illegal, yet Jim Crow remained in effect. When attempts to integrate Selma’s dining and entertainment venues were resumed, blacks who tried to attend the movie theater and eat at a hamburger stand were beaten and arrested.
On July 6, John Lewis led 50 blacks to the courthouse on registration day, but Sheriff Clark arrested them rather than allow them to apply to vote. On July 9, Judge James Hare issued an injunction forbidding any gathering of three or more people under the sponsorship of civil rights organizations or leaders. This injunction made it illegal to even talk to more than two people at a time about civil rights or voter registration in Selma, suppressing public civil rights activity there for the next six months.
With civil rights activity blocked by Judge Hare’s injunction, the DCVL requested the assistance of King and the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC). Three of SCLC’s main organizers – Director of Direct Action and Nonviolent Education James Bevel, Diane Nash, and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/James_Orange James Orang, who had been working on Bevel’s Alabama Voting Rights Project since late 1963, a project which King and the executive board of SCLC had not joined. When SCLC officially accepted Amelia Boynton’s invitation to bring their organization to Selma, Bevel, Nash, Orange and others in SCLC began working in Selma in December 1964. They also worked in the surrounding counties along with the SNCC staff who had been active there since early 1963.
The Selma Voting Rights Movement officially started on January 2, 1965, when King addressed a mass meeting in Brown Chapel in defiance of the anti-meeting injunction.
Over the following weeks, SCLC and SNCC activists expanded voter registration drives and protests in Selma and the adjacent Black Belt counties. In addition to Selma, marches and other protests in support of voting rights were held in Perry, Wilcox, Marengo, Greene, and Hale counties.
On February 18, 1965, an Alabama State Trooper, corporal James Bonard Fowler, shot Jimmie Lee Jackson as he tried to protect his mother and grandfather in a café to which they had fled while being attacked by troopers during a nighttime civil rights demonstration in Marion, the county seat of Perry County. Jackson died eight days later, of an infection resulting from the gunshot wound, at Selma’s Good Samaritan Hospital.
In response, James Bevel called for a march from Selma to Montgomery.
Bevel’s initial plan was to march to Montgomery to ask Governor George Wallace if he had anything to do with ordering the lights out and the state troopers to shoot during the march in which Jackson was killed. Bevel called the march in order to focus the anger and pain of the people of Selma, some of whom wanted to address Jackson’s death with violence, towards a nonviolent goal. The marchers also hoped to bring attention to the violations of their rights by marching to Montgomery. Dr. King agreed with Bevel’s plan, and asked for a march from Selma to Montgomery to ask Governor Wallace to protect black registrants.
Wallace denounced the march as a threat to public safety and declared he would take all measures necessary to prevent this from happening.
The First March: “Bloody Sunday”
On March 7, 1965, 525 to 600 civil rights marchers headed east out of Selma on U.S. Highway 80. The march was led by John Lewis of SNCC and the Reverend Hosea Williams of SCLC, followed by Bob Mants of SNCC and Albert Turner of SCLC. The protest went smoothly until the marchers crossed the Edmund Pettus Bridge and found a wall of state troopers waiting for them on the other side. Their commanding officer told the demonstrators to disband at once and go home. Williams tried to speak to the officer, but the man curtly informed him there was nothing to discuss. Seconds later, the troopers began shoving the demonstrators. Many were knocked to the ground and beaten with nightsticks. Another detachment of troopers fired tear gas. Mounted troopers charged the crowd on horseback.
Brutal televised images of the attack, which presented people with horrifying images of marchers left bloodied and severely injured, roused support for the U.S. civil rights movement. Amelia Boynton was beaten and gassed nearly to death; her photo appeared on the front page of newspapers and news magazines around the world Seventeen marchers were hospitalized, leading to the naming of the day “Bloody Sunday”.
Mar 07 2013
Holder: The President Can Kill You
Cross posted from The Stars Hollow Gazette
I’m not a fan of Rand Paul, the Tea Party backed Republican Senator from Kentucky but I have to give him credit for pushing for an answer to his question “whether the president has the power to authorize lethal force, such as a drone strike, against a US citizen on US soil.” Sen. Paul sent three letters to CIA director nominee John Brennan and finally got his answer from Brennan and from Attorney General Eric Holder. The answer, in so many words, yes, he can and on American soil without due process.

Click on image to enlarge
The Obama administration has asserted that it believes that “under an extraordinary circumstance,” it has the power to assassinate an American citizen on American soil using lethal force.
…It is possible, I suppose, to imagine an extraordinary circumstance in which it would be necessary and appropriate under the Constitution and applicable laws of the United States for the President to authorize the military to use lethal force within the territory of the United States. For example, the President could conceivably have no choice but to authorize the military to use such force if necessary to protect the homeland in the circumstances of a catastrophic attack like the ones suffered on December 7, 1941, and September 11, 2001…
Sen. Paul was appalled at Mr. Holder’s response, “The U.S. Attorney General’s refusal to rule out the possibility of drone strikes on American citizens and on American soil is more than frightening – it is an affront the Constitutional due process rights of all Americans.”
At FDL’s The Dissenter, Kevin Gosztola had his observation about the letter:
Though Holder noted the country’s “long history of using the criminal justice system to incapacitate individuals located” in America “who pose a threat to the United States” and he contended “the use of military force” would be rejected “where well-established law enforcement authorities in the country provide the best means for incapacitating the terrorist threat,” the mere fact that his answer was a yes is outrageous. However, it fits the framework for fighting a permanent global “War on Terrorism” without any geographical limitations, which the Obama administration has maintained it has the authority to wage.
Guardian writer Glenn Greenwald, speaking at the Freedom to Connect conference, said today, “There is a theoretical framework being built that posits that the US Government has unlimited power, when it comes to any kind of threats it perceives, to take whatever action against them that it wants without any constraints or limitations of any kind.”
Paul had to send three letters to Brennan and the question had to be raised by someone in a Google+ chat with the president before the Obama administration would give something resembling an appropriate answer because, as Greenwald suggested saying “yes” would “illustrate the real radicalism that the government has embraced in terms of how it uses its own power.” If they said “no,” it would “jeopardize this critical theoretical foundation that they very carefully have constructed that says there are no cognizable constraints on how US government power can be asserted.”
As it turns out, Holder, the Justice Department and the wider Obama administration opted to not jeopardize the framework.
What Charles Pierce said
This is that into which we have rendered ourselves. As a democracy, we now debate only what kind of monsters we may decide we have to be.
Mar 07 2013
Today on The Stars Hollow Gazette

Our regular featured content-
- On This Day In History March 6 by TheMomCat
- Punting the Pundit by TheMomCat
These featured articles-
- Untouchable by ek hornbeck
- Holder: The President Can Kill You by TheMomCat
- U.S. Implicated In Iraqi Police Torture by ek hornbeck
- Yes, the Sequester is President Obama’s Fault. These are facts. by priceman
Follow us on Twitter @StarsHollowGzt
Write more and often. This is an Open Thread.
Mar 06 2013
Stuck in the Wrong Conversation
Cross posted from The Stars Hollow Gazette
Even though I’m an “only child,” I had a large extended family that we visited quite often, especially my maternal great grandmother and her two maiden sisters. They would gather in the dining room every afternoon for tea and exchange the “news of the day.” Since they were all profoundly hard of hearing, the disconnected conversations were quite amusing and memorable, as you can imagine, even for a five year old.
The conversation about sequester and the manufactured debt/deficit crisis reminded me of the three elderly ladies sitting around that table, talking to each other but not hearing a word the others are saying. The president, congressional leaders and the press are all talking but not hearing what they need to hear and ignoring what the American people want, jobs.
In the middle of the implementation of austere sequestration cuts, we’ve had the inane distraction of the Washington Post‘s columnist Bob Woodward’s “poutrage” which is just another example, as the Washington Post‘s Greg Sargent in the Plum Line puts it, of being stuck in the wrong conversation:
The Woodward flap is superficially an argument about the meaning of Gene Sperling’s email, but as Jonathan Cohn details this morning, this is just a distraction from the broader, far more consequential argument over who is to blame for the creation of sequestration. The answer, of course, is that both sides are to blame for creating it – though one side is far more to blame for the failure to avert it – thanks to the deficit mania that gripped Washington in 2011, at precisely the time we should have been focused on unemployment and economic growth.
Meanwhile, the fact that sequestration is set to hit is a concrete reminder that we’re still stuck with the consequences of that misguided 2011 mindset. Indeed, the continuing argument over how to avert sequestration – whether to replace it with a mix of spending cuts and new revenues, or with just spending cuts – is itself a sign of the continuing power of elite consensus deficit-obsession. After all, the battle is still being fought on deficit/austerity turf, at a time of near-zero growth and mass unemployment, rather than over what government should be doing to boost the economy and alleviate widespread economic suffering. As Atrios has put it, we’re not debating whether to implement more austerity; we’re debating over how much austerity to implement.
Nobel Prize winning economist and New York Times columnist Paul Krugman told Ed Shultz, host of MSNBC’s “Ed Show, “that sequestration was “designed to be stupid” and “this is exactly what the doctor did not order”.
While the spending cuts were conceived as a fix for the federal deficit, Krugman said, this was not the time to implement that kind of measure. Instead, he said, the government should be taking advantage of low interest rates and a high number of unemployed construction workers to invest in infrastructure and education.
“What kind of spending would it take to keep us on the track that we’re on right now?” Schultz asked, noting a continued pattern of private sector job growth despite Republican resistance to a new jobs bill since the stimulus package of 2009.
“If we would just stop cutting, the growth would probably keep going,” Krugman answered. “If spending had grown as fast in this recovery as it has in past recoveries, we’d be spending something like $200 billion a year – state, local and federal – more, maybe $300 billion a year more. Maybe $300 billion a year more. We’d have about a million and a half more public sector workers than we do right now, because we’ve been laying them off at [an] unprecedented pace. So, I think $300 billion a year of additional spending would be appropriate and would mean, if we did it, that we would be pretty close to full employment at this point.”
Talking Points Memo‘s Brian Beutler says that the president has done “excellent job” of “of flipping the politics of taxation to make the GOP’s once bulletproof position a vulnerability,” but the president is still not saying what the public needs to hear about jobs and the social safety net.
Mar 06 2013
Congressional Game of Chicken: Government Shut Down
Cross posted from The Stars Hollow Gazette
Sequestration wasn’t going to happen according to Pres. Barack Obama, but it did. Mostly, because he was naive enough to think that the Republicans would cave because he dangled cuts to Social Security under there noses. Well, that didn’t work out so well. The Tea Party hard liners were adamant about no new taxes and House Speaker John Boehner (R-OH), eager to hold onto his gavel, stood his ground.
We now move to the next manufactured budget crisis on the agenda: the continuing resolution (CR) to keep the government lights on after March 27. If you think that is going to be smooth sailing then you aren’t paying attention. The fight over sequestration could very well lead to a government shutdown:
An aide to Speaker John Boehner (R-OH) said GOP leaders haven’t yet settled on an approach to funding the government. And House Republicans are divided enough that it’s unclear whether they could pass a stripped-down appropriations measure to begin with. Many Republicans would like to use the appropriations process to mitigate sequestration’s defense cuts, or eliminate them by cutting more deeply into domestic spending – a non-starter for Democrats. [..]
“We have had a law that’s in effect; it’s called sequestration,” (Senate Majority Leader Harry Reid (D-NV) said. “Those cuts will go forward. They’re all cuts. I think we need some revenue to take the pressure off everybody. The American people agree with me. And until there’s some agreement on revenue, I believe we should just go ahead with the sequester.”
In other words, Democrats won’t allow Republicans to use a continuing resolution to enshrine sequestration’s lower overall spending requirement by apportioning the cuts in a less indiscriminate way.
Pres. Obama thinks a government shut down can be avoided believing that the Republicans will do the “right thing” and agree to a CR that “adhere to the spending levels they agreed to during the debt limit fight in 2011“:
If House Republicans can’t pass a government funding bill that sets overall spending at levels agreed to in the Budget Control Act – funding that would automatically be reduced because of sequestration – then the government will shutdown and the pressure Republicans feel to cut a deal that both averts sequestration and keeps the government running will intensify. [..]
Thus, if Republicans try to rejigger the sequestration cuts such that they make the lower overall spending levels permanent, but rescind its indiscriminate cutting mechanism and thus remove the pressure on Congress to pass a balanced alternative, they’ll set off a government shutdown fight.
But if Republicans can pass a government funding bill that adheres to spending levels agreed to and set in 2011, then the government will stay open and the fight over sequestration will continue indefinitely.
However the fight over ongoing funding of the government shakes out, Obama said he hopes public pressure convinces Republicans to relent on revenues so that he and Congress can replace sequestration with an alternative deficit reduction plan.
First, the Republicans don’t care about public pressure Second, if Pres. Obama isn’t aware of that then he hasn’t been paying attention and his prediction that the government won’t shut down is as premature as the one about sequestration not happening.
“We agreed to a certain amount of money that was going to be spent each year, and certain funding levels for our military, our education system, and so forth,” Obama said. “If we stick to that deal, then I will be supportive of us sticking to that deal.”
But the implementation of sequestration, particularly its indiscriminate cuts to defense programs, calls into question whether House Republicans will be able to honor the government funding deal without relying on a significant number of Democratic votes. Republicans want to restore some funding to defense programs to mitigate sequestration’s impact on GOP priorities. And that could leave Boehner to choose between keeping his conference united – and thus passing a continuing resolution that the Senate and White House reject – or ignoring internal GOP politics and teaming up with Democrats to keep the government open.
The Republicans in the House have other ideas and have already started planning their end run around the cuts in sequestration they didn’t like by eliminating them in the CR. According to The Hill, they’ve already introduced a funding bill that will “cushion the Pentagon and other agencies from the blow of $85 billion in sequester spending cuts”
It would shift about $10.4 billion into the Pentagon’s operations and maintenance account by cutting other defense accounts, including a $3.6 billion reduction in personnel funds, $2.5 billion less in research and development, and $4.2 billion less in equipment procurement. [..]
In total, the bill includes $518 billion for defense, $2 billion more than President Obama requested this year but the same as in 2012. It assumes the 13 percent cut to non-exempt budget accounts called for by sequestration will occur.
The Republicans are trying to undo the cuts they don’t like while preserving the cuts that the Democrats don’t like and using the CR as an end run around the law.
The Democrats are still reviewing the proposal and have said that they would insist on the same “cushion” non-defense appropriations. There are two scenarios for how this “drama” will play out:
A fight ensues between the House and Senate over the cushions for the Republican’s pet cuts and the Democratic opposition without similar concessions leading to a government shutdown;
Harry Reid gets his orders from the White House, fearing the repercussions of a government shut down, and he puts the House bill up for a vote and it passes with minimum Democratic support.
I’m betting on the latter because Barack already said so.
Mar 06 2013
On This Day In History March 6
Cross posted from The Stars Hollow Gazette
This is your morning Open Thread. Pour your favorite beverage and review the past and comment on the future.
Find the past “On This Day in History” here.
March 6 is the 65th day of the year (66th in leap years) in the Gregorian calendar. There are 300 days remaining until the end of the year.
On this day in 1857, the US Supreme Court hands down its decision on Sanford v. Dred Scott, a case that intensified national divisions over the issue of slavery.
Dred Scott v. Sandford, 60 U.S. 393 (1857), was a ruling by the U.S. Supreme Court that people of African descent imported into the United States and held as slaves (or their descendants, whether or not they were slaves) were not protected by the Constitution and could never be U.S. citizens. The court also held that the U.S. Congress had no authority to prohibit slavery in federal territories and that, because slaves were not citizens, they could not sue in court. Furthermore, the Court ruled that slaves, as chattels or private property, could not be taken away from their owners without due process. The Supreme Court’s decision was written by Chief Justice Roger B. Taney.
Although the Supreme Court has never overruled the Dred Scott case, the Court stated in the Slaughter-House Cases of 1873 that at least one part of it had already been overruled by the Fourteenth Amendment in 1868:
The first observation we have to make on this clause is, that it puts at rest both the questions which we stated to have been the subject of differences of opinion. It declares that persons may be citizens of the United States without regard to their citizenship of a particular State, and it overturns the Dred Scott decision by making all persons born within the United States and subject to its jurisdiction citizens of the United States.
The Supreme Court ruling was handed down on March 6, 1857, just two days after Buchanan’s inauguration. Chief Justice Taney delivered the opinion of the Court, with each of the concurring and dissenting Justices filing separate opinions. In total, six Justices agreed with the ruling; Samuel Nelson concurred with the ruling but not its reasoning, and Benjamin R. Curtis and John McLean dissented. The court misspelled Sanford’s name in the decision.
The Court first had to decide whether it had jurisdiction. Article III, Section 2, Clause 1 of the U.S. Constitution provides that “the judicial Power shall extend… to Controversies… between Citizens of different States….” The Court held that Scott was not a “citizen of a state” within the meaning of the United States Constitution, as that term was understood at the time the Constitution was adopted, and therefore not able to bring suit in federal court. Furthermore, whether a person is a citizen of a state, for Article III purposes, was a question to be decided by the federal courts irrespective of any state’s definition of “citizen” under its own law.
Thus, whether Missouri recognized Scott as a citizen was irrelevant. Taney summed up,
Consequently, no State, since the adoption of the Constitution, can by naturalizing an alien invest him with the rights and privileges secured to a citizen of a State under the Federal Government, although, so far as the State alone was concerned, he would undoubtedly be entitled to the rights of a citizen, and clothed with all the rights and immunities which the Constitution and laws of the State attached to that character.
This meant that
no State can, by any act or law of its own, passed since the adoption of the Constitution, introduce a new member into the political community created by the Constitution of the United States.
The only relevant question, therefore, was whether, at the time the Constitution was ratified, Scott could have been considered a citizen of any state within the meaning of Article III. According to the Court, the authors of the Constitution had viewed all blacks as
beings of an inferior order, and altogether unfit to associate with the white race, either in social or political relations, and so far inferior that they had no rights which the white man was bound to respect.
The Court also presented a parade of horribles argument as to the feared results of granting Mr. Scott’s petition:
It would give to persons of the negro race, …the right to enter every other State whenever they pleased, …the full liberty of speech in public and in private upon all subjects upon which its own citizens might speak; to hold public meetings upon political affairs, and to keep and carry arms wherever they went.
Scott was not a citizen of Missouri, and the federal courts therefore lacked jurisdiction to hear the dispute.
Despite the conclusion that the Court lacked jurisdiction, however, it went on to hold (in what Republicans would label its “obiter dictum”) that Scott was not a free man, even though he had resided for a time in Minnesota (then called the Wisconsin Territory). The Court held that the provisions of the Missouri Compromise declaring it to be free territory were beyond Congress’s power to enact. The Court rested its decision on the grounds that Congress’s power to acquire territories and create governments within those territories was limited. They held that the Fifth Amendment barred any law that would deprive a slaveholder of his property, such as his slaves, because he had brought them into a free territory. The Court went on to state – although the issue was not before the Court – that the territorial legislatures had no power to ban slavery. The ruling also asserted that neither slaves “nor their descendants, were embraced in any of the other provisions of the Constitution” that protected non-citizens.
This was only the second time in United States history that the Supreme Court had found an act of Congress to be unconstitutional. (The first time was 54 years earlier in Marbury v. Madison).
Mar 06 2013
In Memoriam: Hugo Chavez 1954 – 2013
 Popular Venezuelan President Hugo Chavez succumbed to cancer today in a hospital in Caracas ending his 14 years as the leader of the oil rich South American country.
Popular Venezuelan President Hugo Chavez succumbed to cancer today in a hospital in Caracas ending his 14 years as the leader of the oil rich South American country.
The flamboyant 58-year-old had undergone four operations in Cuba for a cancer that was first detected in his pelvic region in mid-2011. His last surgery was on December 11 and he had not been seen in public since. [..]
Chavez easily won a new six-year term at an election in October and his death will devastate millions of supporters who adored his charismatic style, anti-U.S. rhetoric and oil-financed policies that brought subsidized food and free health clinics to long-neglected slums.
Pres. Chavez was certainly controversial but it was through his economic and social policies that Venezuela reduced the poverty level from a low of 55.44% in 1998 to 26 percent at the end of 2008. Extreme poverty fell by 72%. He increased access to health care and education. In 2003, he made food security a priority by opening a nation wide chain of supermarkets and setting price ceilings for basic staple foods.
Pres. Chavez’ human rights record was somewhat mixed:
In the 1999 Venezuelan constitution, 116 of 300 articles were concerned with human rights; these included increased protections for indigenous peoples and women, and established the rights of the public to education, housing, healthcare, and food. It called for dramatic democratic reforms such as ability to recall politicians from office by popular referendum, increased requirements for government transparency, and numerous other requirements to increase localized, participatory democracy, in favor of centralized administration. It gave citizens the right to timely and impartial information, community access to media, and a right to participate in acts of civil disobedience.
However, as recently as 2010, Amnesty International has criticized the Chávez administration for targeting critics following several politically motivated arrests. Freedom House lists Venezuela as being “partly free” in its 2011 Freedom in the World annual report, noting a recent decline in civil liberties. A 2010 Organization of American States report found concerns with freedom of expression, human rights abuses, authoritarianism, press freedom, threats to democracy, as well as erosion of separation of powers, the economic infrastructure and ability of the president to appoint judges to federal courts.
Born Hugo Rafael Chávez Frías into a working-class family in Sabaneta, Barinas, he is survived by two ex-wives, Nancy Colmenares and Marisabel Rodríguez, and four children – Hugo Rafael, María Gabriela and Rosa Virginia by his first wife and Rosinés by his second.
Blessed Be. The Wheel Turns
Mar 05 2013
Today on The Stars Hollow Gazette

Our regular featured content-
- On This Day In History March 5 by TheMomCat
- Punting the Pundit by TheMomCat
These featured articles-
- Stuck in the Wrong Conversation by TheMomCat
- Congressional Game of Chicken: Government Shut Down by TheMomCat
- “Strengthening Social Security” and Other Euphemisms by joe shikspack
Follow us on Twitter @StarsHollowGzt
Write more and often. This is an Open Thread.
Mar 05 2013
On This Day In History March 5
This is your morning Open Thread. Pour your favorite beverage and review the past and comment on the future.
Find the past “On This Day in History” here.
March 5 is the 64th day of the year (65th in leap years) in the Gregorian calendar. There are 301 days remaining until the end of the year.
On this day in 1770, a mob of angry colonists gathers at the Customs House in Boston and begins tossing snowballs and rocks at the lone British soldier guarding the building. The protesters opposed the occupation of their city by British troops, who were sent to Boston in 1768 to enforce unpopular taxation measures passed by a British parliament without direct American representation.
The event began on King Street, today known as State Street, in the early evening of March 5, in front of Private Hugh White, a British sentry, as he stood duty outside the Custom house. A young wigmaker’s apprentice named Edward Gerrish called out to a British officer, Captain Lieutenant John Goldfinch, that Goldfinch had not paid the bill of Gerrish’s master. Goldfinch had in fact settled his account and ignored the insult. Gerrish departed, but returned a couple of hours later with companions. He continued his complaints, and the civilians began throwing rocks at Goldfinch. Gerrish exchanged insults with Private White, who left his post, challenged the boy, and struck him on the side of the head with a musket. As Gerrish cried in pain, one of his companions, Bartholomew Broaders, began to argue with White. This attracted a larger crowd.
As the evening progressed, the crowd grew larger and more boisterous. The mob grew in size and continued harassing Private White. As bells, which usually signified a fire, rang out from the surrounding steeples, the crowd of Bostonians grew larger and more threatening. Over fifty of the Bostonian townsmen gathered and provoked White and Goldfinch into fight. As the crowd began to get larger, the British soldiers realized that the situation was about to explode. Private White left his sentry box and retreated to the Custom House stairs with his back to a locked door. Nearby, from the Main Guard, the Officer of the Day, Captain Thomas Preston, watched this situation escalate and, according to his account, dispatched a non-commissioned officer and seven or eight soldiers of the 29th Regiment of Foot, with fixed bayonets, to relieve White. He and his subordinate, James Basset, followed soon afterward. Among these soldiers were Corporal William Wemms (apparently the non-commissioned officer mentioned in Preston’s report), Hugh Montgomery, John Carroll, James Hartigan, William McCauley, William Warren and Matthew Kilroy. As this relief column moved forward to the now empty sentry box, the crowd pressed around them. When they reached this point they loaded their muskets and joined with Private White at the custom house stairs. As the crowd, estimated at 300 to 400, pressed about them, they formed a semicircular perimeter.
The crowd continued to harass the soldiers and began to throw snow balls and other small objects at the soldiers. Private Hugh Montgomery was struck down onto the ground by a club wielded by Richard Holmes, a local tavernkeeper. When he recovered to his feet, he fired his musket, later admitting to one of his defense attorneys that he had yelled “Damn you, fire!” It is presumed that Captain Preston would not have told the soldiers to fire, as he was standing in front of the guns, between his men and the crowd of protesters. However, the protesters in the crowd were taunting the soldiers by yelling “Fire”. There was a pause of indefinite length; the soldiers then fired into the crowd. Their uneven bursts hit eleven men. Three Americans – ropemaker Samuel Gray, mariner James Caldwell, and a mixed race sailor named Crispus Attucks – died instantly. Seventeen-year-old Samuel Maverick, struck by a ricocheting musket ball at the back of the crowd, died a few hours later, in the early morning of the next day. Thirty-year-old Irish immigrant Patrick Carr died two weeks later. To keep the peace, the next day royal authorities agreed to remove all troops from the centre of town to a fort on Castle Island in Boston Harbor. On March 27 the soldiers, Captain Preston and four men who were in the Customs House and alleged to have fired shots, were indicted for murder.
At the request of Captain Preston and in the interest that the trial be fair, John Adams, a leading Boston Patriot and future President, took the case defending the British soldiers.
In the trial of the soldiers, which opened November 27, 1770, Adams argued that if the soldiers were endangered by the mob, which he called “a motley rabble of saucy boys, negroes, and molattoes, Irish teagues and outlandish jack tarrs,” they had the legal right to fight back, and so were innocent. If they were provoked but not endangered, he argued, they were at most guilty of manslaughter. The jury agreed with Adams and acquitted six of the soldiers. Two of the soldiers were found guilty of manslaughter because there was overwhelming evidence that they fired directly into the crowd, however Adams invoked Benefit of clergy in their favor: by proving to the judge that they could read by having them read aloud from the Bible, he had their punishment, which would have been a death sentence, reduced to branding of the thumb in open court. The jury’s decisions suggest that they believed the soldiers had felt threatened by the crowd. Patrick Carr, the fifth victim, corroborated this with a deathbed testimony delivered to his doctor.
Three years later in 1773, on the third anniversary of the incident, John Adams made this entry in his diary:
The Part I took in Defence of Cptn. Preston and the Soldiers, procured me Anxiety, and Obloquy enough. It was, however, one of the most gallant, generous, manly and disinterested Actions of my whole Life, and one of the best Pieces of Service I ever rendered my Country. Judgment of Death against those Soldiers would have been as foul a Stain upon this Country as the Executions of the Quakers or Witches, anciently. As the Evidence was, the Verdict of the Jury was exactly right.
“This however is no Reason why the Town should not call the Action of that Night a Massacre, nor is it any Argument in favour of the Governor or Minister, who caused them to be sent here. But it is the strongest Proofs of the Danger of Standing Armies.
Mar 05 2013
Austerity Could End The Death Penalty
Cross posted from The Stars Hollow Gazette
Someone has finally found the argument that could finally put an end to the death penalty, it costs too much. In the age of austerity, the cost to the state of Maryland to litigate the appeal of inmates on death row is three times higher than the cost of life in prison without parole:
In its 2008 report, the (Maryland Commission on Capital Punishment) wrote that the average cost of prosecuting and imprisoning a Death Row inmate was $3 million, nearly three times higher than the cost of convicting and sentencing a murderer to life imprisonment. Of that $3 million, $1.7 million is spent in the courtroom and $1.3 million is spent in a Supermax prison, the commission wrote. [..]
The commission determined that the state spent $1.8 million dollars for every failed attempt to impose the death penalty, including $950,000 in prison costs and $850,000 in adjudication costs.
Maryland’s Gov. Martin O’Malley said since the death penalty is not a crime deterrent and the exorbitant cost, it is time to end the death penalty in his state.
On Friday, the Maryland state Senate once again began debating a bill to repeal capital punishment in the state. It needs 24 votes to pass and 26 senators have already said publicly that they support the repeal.
Rather than funnel all of their focus into moral and social arguments, the bill’s supporters have been making their point partly in economic terms. The cost of prosecuting a death row case in Maryland can be as much as three times what it costs for a case seeking a life sentence without parole.
On Sunday’s Up with Chris Hayes, Bryan Stevenson, founder & executive Director of Equal Justice Initiative, professor at New York University School of Law, addressed how the savings could benefit public safety. He and Up host Chris Hayes were joined by panelists Mattea Kramer, the National Priorities Project; David Sirota, contributor to Salon.com; and Roberto Lovato, writer for New American Media, contributor to The Nation.


