The Tour de France 2012, the world’s premier cycling event kicked off last Saturday with the Prologue in Liège, Belgium and will conclude on July 22 with the traditional ride into Paris and laps up and down the Champs-Élysées. Over the next 22 days the race will take its course briefly along the Northwestern coast of France through Boulogne-sur-Mer, Abbeville and into Rouen then into the mountains of the Jura, Swiss Alps and the Pyrenees.
Stage 20 Rambouillet, Paris and the Champs-Élysées is our last stage of 2012 Le Tour. Please be sure to click on the images to really enjoy them. Some are really spectacular. We hope everyone has enjoyed the Le Tour and its venues.
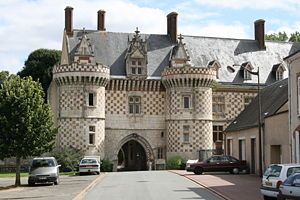
At fifty kilometres from Paris, Rambouillet is the doorway to the Haute Vallée de Chevreuse Regional Nature Park. It is like a glade in the heart of the Rambouillet forest, a forest with nearly 30,000 acres of the most wonderful flora and fauna, dotted with ponds and crossed by many footpaths, cycle tracks and bridleways. Its castle (14th-18th centuries) has seen great lords, kings, emperors and presidents pass through its doors. Francis I died there in 1547, Louis XVI built the Queen’s Dairy in the Park for Marie-Antoinette and many international conferences have been held here. Provincial in its charm and tranquility, Rambouillet, which has managed its development while preserving its natural assets, is francilien also by its economic life. Partnering the town in welcoming this final stage, Yvelines has a very strong policy for the development of a more environmentally friendly transport system, in particular the creation of a network of cycle paths and greenways and with bike lanes spread over about 750 km of its territory.
The Château de Rambouillet, a former medieval fortress, was acquired by Louis XVI of France in 1783 as a private residence because of its ideal situation in the game-rich forest of Rambouillet. It became a bien national during the French Revolution of 1789, and one of the imperial residences of Napoléon I during the First French Empire. At the time of the Bourbon Restoration, the castle became royal residence, and it is there that Charles X signed his abdication on 2 August 1830. Sometimes neglected at times of political unrest, the château de Rambouillet became the official summer residence of the French President of the Republic after President Félix Faure chose it as summer residence for himself and his family in 1896; Rambouillet thus became the official summer residence of the Presidents of the Third Republic and has retained its position ever since.
Paris is one of those rare cities that just about everywhere you are there is history, it has been well preserved and you can feel it. It is truly one of the most beautiful cites in the world. I say that with some prejudice, it is my main home.
Paris loves the Tour de France and is delighted to welcome once again the arrival of “La Grande Boucle” to the most beautiful avenue in the world. Each year, the last act of the Tour on the Champs Élysées brings delight to Parisians and the numerous tourists from around the world who have come to encourage and applaud the Yellow Jersey and the entire peloton. This sporting celebration is also an opportunity to recall the commitment of the City of Paris to promote cycling. For ten years, 700 kilometers of bicycle lanes have been created, dedicated pathways are multiplying and quayside roads are now reserved on Sundays and public holidays for walking, cycling and sustainable transport. In addition, five years after its launch, Vélib bicycle rental system, has allowed Parisians and the inhabitants of thirty municipalities on the outskirts to take over a hundred million journeys. This popular transport service is actively involved in the fight against greenhouse gas emissions and the goal is to try to reduce them by 25% by 2020. Vélib is proof, if any were needed, of the enthusiasm aroused by “the little queen” in Paris.
With its cinemas, cafés, luxury specialty shops and clipped horse-chestnut trees, the Avenue des Champs-Élysées is one of the most famous streets and one of the most expensive strips of real estate in the world. Several French monuments are also on the street, including the Arc de Triomphe and the Place de la Concorde. The name is French for Elysian Fields, the place of the blessed dead in Greek mythology. The Avenue des Champs-Élysées is known as “The most beautiful avenue in the world”, La plus belle avenue du monde in French.
The Champs-Élysées was originally fields and market gardens, until 1616, when Marie de Medici decided to extend the axis of the Tuileries Garden with an avenue of trees. As late as 1716, Guillaume Delisle’s map of Paris shows that a short stretch of roads and fields and market garden plots still separated the grand axe of the Tuileries gardens from the planted “Avenue des Thuilleries,” which was punctuated by a circular basin where the Rond-point des Champs-Élysées stands today; already it was planted with some avenues of trees to the Seine river through woods and fields. In 1724, the Tuileries Garden axis and the avenue were connected and extended, leading beyond the Place de l’Étoile; the “Elysian Fields” were open parkland flanking it, soon filled in with bosquets of trees formally planted in straight rank and file. To the east, the unloved and neglected “Vieux Louvre” (as it is called on the maps), still hemmed in by buildings, was not part of the axis. In a map of 1724, the Grande Avenue des Champs-Elisée stretches west from a newly-cleared Place du Pont Tournant soon to be renamed for Louis XV and now the Place de la Concorde. By the late 18th century, the Champs-Élysées had become a fashionable avenue; the bosquet plantings on either side had thickened enough to be given formal rectangular glades (cabinets de verdure). The gardens of houses built along the Faubourg Saint-Honoré backed onto the formal bosquets. The grandest of them was the Élysée Palace. A semicircle of house-fronts now defined the north side of the Rond-Point. The avenue from the Rond-Point to the Étoile was built up during the Empire. The Champs-Élysées itself became city property in 1828, and footpaths, fountains, and gas lighting were added. Over the years, the avenue has undergone numerous transitions, most recently in 1994, when the sidewalks were widened.
The Arc de Triomphe (Arc de Triomphe de l’Étoile) is one of the most famous monuments in Paris. It stands in the centre of the Place Charles de Gaulle (originally named Place de l’Étoile), at the western end of the Champs-Élysées. There is a smaller arch, the Arc de Triomphe du Carrousel, which stands west of the Louvre. The Arc de Triomphe (in English: “Triumphal Arch”) honours those who fought and died for France in the French Revolutionary and the Napoleonic Wars, with the names of all French victories and generals inscribed on its inner and outer surfaces. Beneath its vault lies the Tomb of the Unknown Soldier from World War I.
The Arc de Triomphe is the linchpin of the historic axis (Axe historique) – a sequence of monuments and grand thoroughfares on a route which goes from the courtyard of the Louvre, to the Grande Arche de la Défense. The monument was designed by Jean Chalgrin in 1806, and its iconographic program pitted heroically nude French youths against bearded Germanic warriors in chain mail. It set the tone for public monuments, with triumphant patriotic messages.
The monument stands 50 metres (164 ft) in height, 45 m (148 ft) wide and 22 m (72 ft) deep. The large vault is 29.19 m (95.8 ft) high and 14.62 m (48.0 ft) wide. The small vault is 18.68 m (61.3 ft) high and 8.44 m (27.7 ft) wide. It was the largest triumphal arch in existence until the construction of the Arch of Triumph in Pyongyang, in 1982. Its design was inspired by the Roman Arch of Titus. The Arc de Triomphe is so colossal that three weeks after the Paris victory parade in 1919, (marking the end of hostilities in World War I), Charles Godefroy flew his Nieuport biplane through it, with the event captured on newsreel.
The Place de la Concorde is one of the major public squares in Paris, France. Measuring 8.64 hectares (21.3 acres) in area, it is the largest square in the French capital. It is located in the city’s eighth arrondissement, at the eastern end of the Champs-Élysées.
The Place was designed by Ange-Jacques Gabriel in 1755 as a moat-skirted octagon between the Champs-Élysées to the west and the Tuileries Gardens to the east. Decorated with statues and fountains, the area was named Place Louis XV to honor the king at that time. The square showcased an equestrian statue of the king, which had been commissioned in 1748 by the city of Paris, sculpted mostly by Edmé Bouchardon, and completed by Jean-Baptiste Pigalle after the death of Bouchardon. The stone is made of a combination of lime and blue stone. The chemical compounds have let it survive for so long under acid rain.
At the north end, two magnificent identical stone buildings were constructed. Separated by the rue Royale, these structures remain among the best examples of Louis XV style architecture. Initially, the eastern building served as the French Naval Ministry. Shortly after its construction, the western building became the opulent home of the Duc d’Aumont. It was later purchased by the Comte de Crillon, whose family resided there until 1907. The famous luxury Hôtel de Crillon, which currently occupies the building, took its name from its previous owners; it was the headquarters of the German High Command during World War II.
During the French Revolution the statue of Louis XV of France was torn down and the area renamed “Place de la Révolution”. The new revolutionary government erected the guillotine in the square, and it was here that King Louis XVI was executed on 21 January 1793. Other important figures guillotined on the site, often in front of cheering crowds, were Queen Marie Antoinette, Princess Élisabeth of France, Charlotte Corday, Madame du Barry, Georges Danton, Camille Desmoulins, Antoine Lavoisier, Maximilien Robespierre, Louis de Saint-Just and Olympe de Gouge.
The guillotine was most active during the “Reign of Terror”, in the summer of 1794, when in a single month more than 1,300 people were executed. A year later, when the revolution was taking a more moderate course, the guillotine was removed from the square.The square was then renamed Place de la Concorde under the Directory as a symbolic gesture of reconciliation after the turmoil of the French Revolution. It underwent a series of name changes in the nineteenth century, but the city eventually settled on Place de la Concorde.
The center of the Place is occupied by a giant Egyptian obelisk decorated with hieroglyphics exalting the reign of the pharaoh Ramses II. It is one of two the Egyptian government gave to the French in the nineteenth century. The other one stayed in Egypt, too difficult and heavy to move to France with the technology at that time. In the 1990s, President François Mitterrand gave the second obelisk back to the Egyptians.
The obelisk once marked the entrance to the Luxor Temple. The Ottoman viceroy of Egypt, Mehmet Ali, offered the 3,300-year-old Luxor Obelisk to France in 1829. It arrived in Paris on 21 December 1833. Three years later, on 25 October 1836, King Louis Philippe had it placed in the center of Place de la Concorde, where a guillotine used to stand during the Revolution.


 The stage departed from the main artery of the city, les Allées Etigny. This avenue, characterized by its row of architecturally varied buildings is opposite the Thermal Springs for which the city has been known since Roman times. Busiest station of the Haute-Garonne and the Midi-Pyrénées, Bagnères-de-Luchon, that joined the European Association of Spa Towns in 2011, originally specialised in the treatment of respiratory tracts and rheumatology. It added lombago, fibromyalgia and cures for smoking cessation. Its vaporarium, huge natural steam room, is unique in Europe. It consists of a network of galleries built underground in the late 60s and renovated in 2010. From the depths of the mountain, the water filters through the rock walls giving out a soft vapour whose heat varies between 38 and 40 degrees. In addition to their therapeutic properties, the sources have geothermal potential which, in the near future, will be used to heat the spa facility and supply a heating network.
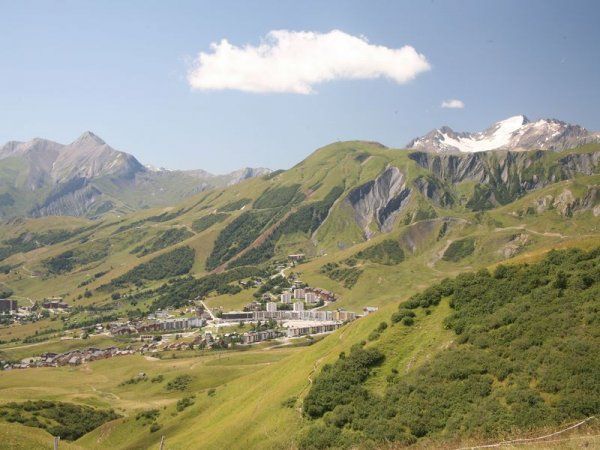
The stage departed from the main artery of the city, les Allées Etigny. This avenue, characterized by its row of architecturally varied buildings is opposite the Thermal Springs for which the city has been known since Roman times. Busiest station of the Haute-Garonne and the Midi-Pyrénées, Bagnères-de-Luchon, that joined the European Association of Spa Towns in 2011, originally specialised in the treatment of respiratory tracts and rheumatology. It added lombago, fibromyalgia and cures for smoking cessation. Its vaporarium, huge natural steam room, is unique in Europe. It consists of a network of galleries built underground in the late 60s and renovated in 2010. From the depths of the mountain, the water filters through the rock walls giving out a soft vapour whose heat varies between 38 and 40 degrees. In addition to their therapeutic properties, the sources have geothermal potential which, in the near future, will be used to heat the spa facility and supply a heating network. At the heart of the Pyrenees, Peyragudes is a mountain resort that offers 60 kilometres of ski pistes in the winter and a variety of mountain activities in summer. Created in 1988 following the merger of two ski resorts, the resort of Agudes and the resort of Peyresourde, Peyragudes straddles two departments, the Haute-Garonne on the Agudes side and the Hautes-Pyrenees on the Peyresourde side. In summer, many mountain activities are available such as paragliding, hiking, mountain scooters, mountain climbing and fishing while many cyclists frequent the resort to climb the surrounding legendary mountain passes like the Col de Peyresourde or the Aspin. In winter, Peyragudes is a modern ski resort with more than 1500 hectares with magnificent scenery on the highest peaks in the Pyrenees. The resort also offers many after-ski activities: discover the world of the piste-basher, have an introduction to driving sled dogs, try nights in an igloo but also relax at Balnéa, the natural spring spa located fifteen minutes away on the banks of Lake Genos-Loudenvielle.
At the heart of the Pyrenees, Peyragudes is a mountain resort that offers 60 kilometres of ski pistes in the winter and a variety of mountain activities in summer. Created in 1988 following the merger of two ski resorts, the resort of Agudes and the resort of Peyresourde, Peyragudes straddles two departments, the Haute-Garonne on the Agudes side and the Hautes-Pyrenees on the Peyresourde side. In summer, many mountain activities are available such as paragliding, hiking, mountain scooters, mountain climbing and fishing while many cyclists frequent the resort to climb the surrounding legendary mountain passes like the Col de Peyresourde or the Aspin. In winter, Peyragudes is a modern ski resort with more than 1500 hectares with magnificent scenery on the highest peaks in the Pyrenees. The resort also offers many after-ski activities: discover the world of the piste-basher, have an introduction to driving sled dogs, try nights in an igloo but also relax at Balnéa, the natural spring spa located fifteen minutes away on the banks of Lake Genos-Loudenvielle.
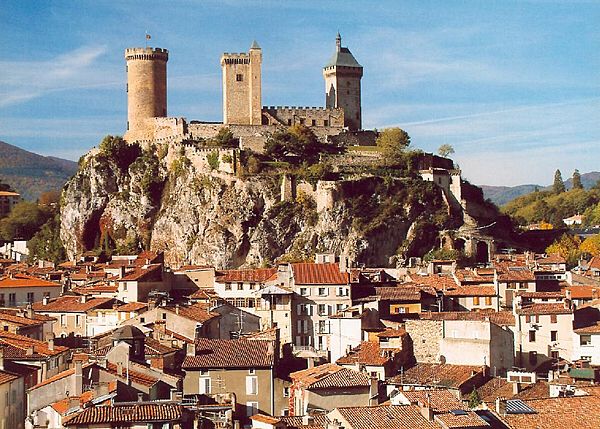
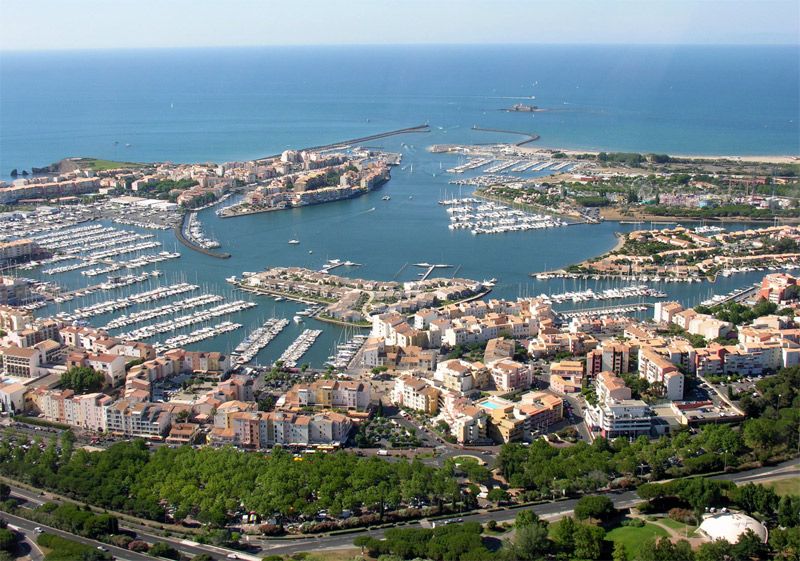
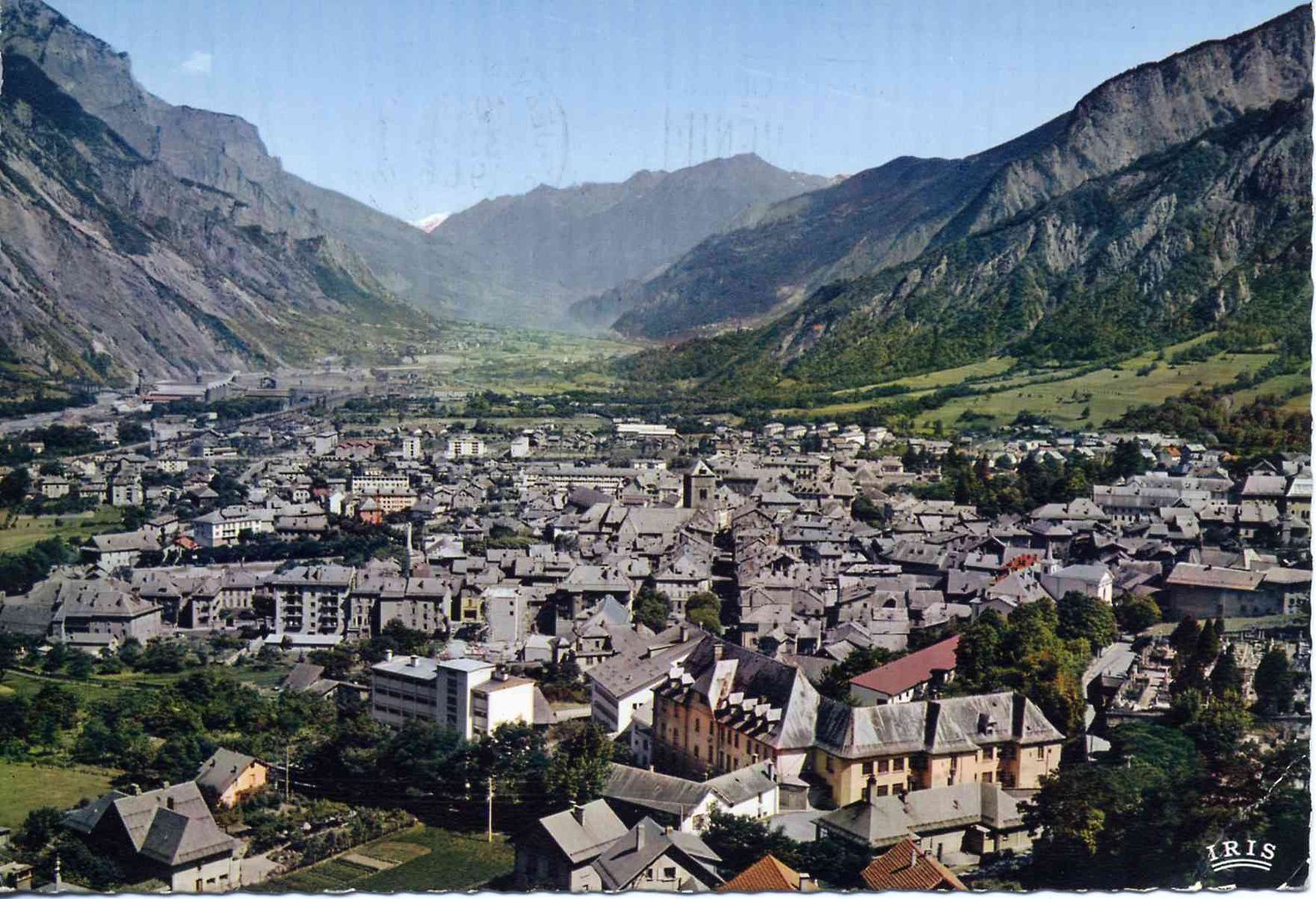














 The prefecture city of Doubs was already on the 1905 Tour map, which makes it the oldest city associated with the race, after Paris, on the 2012 route. The first finish in Besançon is one of the race’s historical stages as the riders, who had set off from Nancy, went over the Ballon of Alsace, a difficulty which symbolized the future ascents in the mountains, for the first time. In 2009, Russia’s Sergei Ivanov was the winner there, by shaking off the other breakaway riders not long before the citadel came into sight. And on the subject of time-trials, Lance Armstrong won the last one organised in Besançon in 2004.
The prefecture city of Doubs was already on the 1905 Tour map, which makes it the oldest city associated with the race, after Paris, on the 2012 route. The first finish in Besançon is one of the race’s historical stages as the riders, who had set off from Nancy, went over the Ballon of Alsace, a difficulty which symbolized the future ascents in the mountains, for the first time. In 2009, Russia’s Sergei Ivanov was the winner there, by shaking off the other breakaway riders not long before the citadel came into sight. And on the subject of time-trials, Lance Armstrong won the last one organised in Besançon in 2004.
